Monetary policy: Definition, types and tools
What is monetary policy?
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank or monetary authority to manage the supply of money and interest rates in an economy, with the aim of promoting economic growth and stability. To affect the price and accessibility of credit, this may entail altering the money supply, setting interest rates or utilizing other instruments.
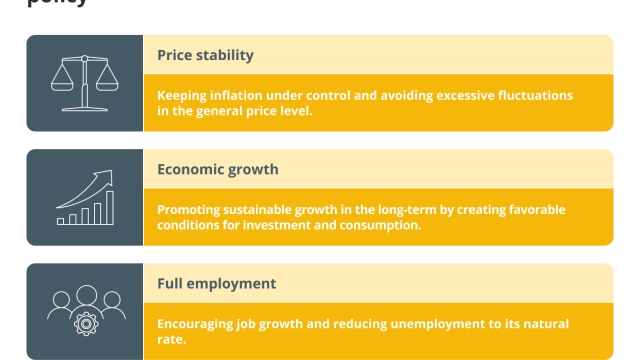
The ultimate goal of monetary policy is to achieve and maintain a healthy economy. This usually involves balancing multiple objectives, such as:

To ensure economic stability, lessen the effects of economic shocks and promote sustainable economic growth, central banks carefully control the money supply and interest rates. However, depending on the unique circumstances and requirements of each economy, monetary policy’s exact goals and tactics may change.
Types of monetary policy
There are two main types of monetary policy:
- Expansionary monetary policy: The goal of an expansionary monetary policy is to boost the money supply and promote economic expansion. Lowering interest rates, expanding the money supply and easing reserve requirements can all be used to achieve this.
- Contractionary monetary policy: It aims to decrease the money supply and control inflation. Raising interest rates, reducing the money supply and boosting reserve requirements can all be used to achieve this.
Different types of monetary policy tools
The tools used to implement monetary policy can be broadly categorized into three types:
- Open market operations: This involves the central bank buying or selling government securities in the open market to increase or decrease the money supply.
- Interest rates: The central bank can change the benchmark interest rate, which is the rate at which banks can borrow from the central bank. This influences other interest rates in the economy, affecting borrowing and spending.
- Reserve requirements: The central bank can change the reserve requirements for banks, which affects the amount of funds banks must hold in reserve and can lend out.
Other tools used less frequently include discount window lending, moral suasion and direct controls on bank lending.
Monetary policy of fiat currency vs. monetary policy of cryptocurrencies
To achieve macroeconomic goals such as price stability, full employment and economic growth, central banks like the Federal Reserve in the United States set and implement monetary policy for fiat currencies. To affect the money supply and demand in the economy, central banks employ a variety of monetary policy measures, including changing interest rates, conducting open market transactions and imposing reserve requirements.
Related: Crypto resonates better with BIS’ vision of ideal monetary system
On the other hand, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) use a decentralized monetary policy, which refers to the approach of controlling the supply of money in a cryptocurrency that is based on decentralized, algorithmic rules, rather than centralized decision-making by a central authority or central bank.
In a decentralized monetary system, mathematical algorithms stored in the cryptocurrency’s software control the creation and circulation of money. This ensures that the money supply remains stable and is not subject to arbitrary changes by a central authority. For instance, Bitcoin is restricted to 21 million, and its creation rate gradually decreases over time.
There are a number of benefits to decentralizing monetary policy as opposed to centralization. By establishing a more stable and predictable monetary policy, it removes the need for faith in a centralized authority and lowers the risk of inflation. Furthermore, it makes it more challenging for governments to manipulate the money supply for purposes of politics or commerce.
Related: What is the economic impact of cryptocurrencies?
However, decentralized monetary policies also have their challenges. They may not be able to react to changes in market conditions rapidly because they are less flexible than centralized monetary policy. Additionally, deflationary pressure from the scarcity of various cryptocurrencies may prevent people from investing and spending money.
What will the monetary policy of CBDCs look like?
Since central banks will be able to modify the quantity of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) to meet their macroeconomic goals, similar to conventional fiat currencies, CBDCs issued by central banks may provide greater control over the money supply and demand than cryptocurrencies. This indicates that central banks may affect the amount of money in circulation and the demand for it in the economy by altering interest rates, conducting open market transactions and imposing reserve requirements.
Related: Wholesale CBDC vs. retail CBDC: Key differences
However, the precise monetary policy of CBDCs would depend on their individual designs and the goals of the central banks issuing them. The monetary policies of some CBDCs may be more open-ended, whereas those of others may be more closely aligned with existing fiat currencies or cryptocurrencies. The developing nature of digital currencies and the requirement for central banks to adopt this new technology will likely ultimately impact the monetary policy of CBDCs.
